Custom Optical Heat Absorbing Glass Grb1 Kg2 Kg5 Optical Shortpass Filters






Custom Optical Heat Absorbing Glass Grb1 Kg2 Kg5 Optical Shortpass Filters
Item Number:X-P23F3T16601
Heat absorbing glass filter is used to reduce heat transfer from the optical system. Heat absorbing glass filters high transmission in the visible wavelength region and absorption in the infrared wavelength region.VY Optoelectronics Co.,Ltd. can customize Heat absorbing filter according to your requirements.
- Dimension: 3mm-300mm
- Thickness: 1.0mmm, 1.10mm
- CWL: 808nm+/-5nm, 920nm, 880nm or as requested
- FWHM: 20nm
- Transmission: 90%
What is Heat Absorbing Filters?
Heat Absorbing Filters feature high transmittance in the visible region and good absorption of heat
rays (infrared rays). They efficiently absorb thermal radiation emitted from light sources and are
highly effective when employed for slide projectors and illumination equipment.
Performance of Heat Absorbing Filters
Heat-absorbing filters in lighting systems get hot during operation. The heat is efficiently dissipated from an optical system by directly cooling or by ventilation of the absorbing filter glass. We recommend the filters' thermal tempering after the polishing and shaping processes whenever heat-absorbing glass must withstand an increased operating temperature.
Application of KG-Filters
KG-Filters not only work in lighting applications. Many other optical systems profit from the exciting properties of these standard SCHOTT glass filter materials. As the KG-absorption glasses have the advantage of a much more broadband blocking of the infrared wavelength range than coated filters (Hot Mirrors), they represent a better solution whenever you want to block a broad IR spectrum
VY Optics Custom Optical Heat Absorbing Glass photo display

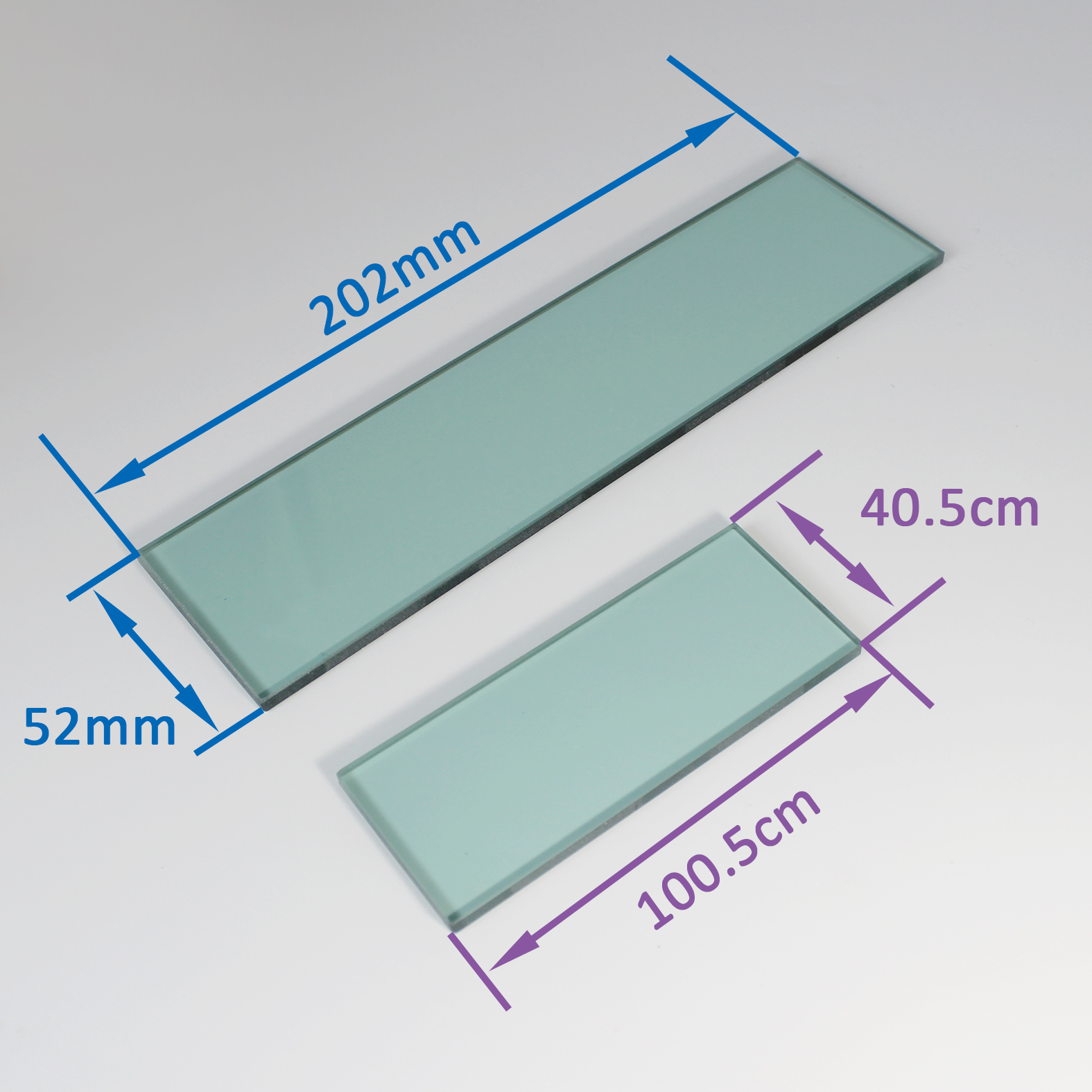
Specifications of optical Kg5 Optical Shortpass Filters
| Material | KG5 |
| Length | 100.5mm/202.0mm |
| Width | 40.2mm/52.0nm |
| Thickness | 4.5nm |
Curves for Schott KG Series Heat Absorbing Glass

Term of Optical Filter
CENTRAL WAVELENGTH
Center Wavelength (CWL), used in defining bandpass filters, describes the midpoint of spectral bandwidth over which the filter transmits. Traditional Coated Optical Filters tend to achieve a maximum transmission near the center wavelength, whereas Hard Coated Optical Filters tend to have a fairly flat transmission profile over the spectral bandwidth.
BANDWIDTH
Bandwidth is a wavelength range used to denote a specific part of the spectrum that passes incident energy through filters.
Bandwidth is also referred to as FWHM (Figure 1).
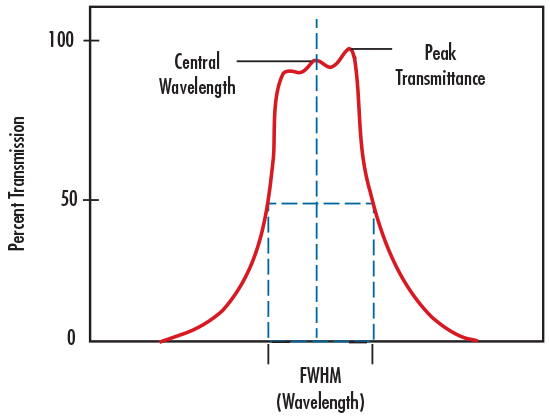
FIGURE 1: ILLUSTRATION OF CENTER WAVELENGTH AND FULL WIDTH AT HALF MAXIMUM
FULL WIDTH-HALF MAXIMUM
Full Width-Half Maximum (FWHM) describes the spectral bandwidth over which a bandpass filter will transmit. The upper and lower limit of that bandwidth is defined at the wavelengths where the filter achieves 50% of the maximum transmission. For example, if the maximum transmission of the filter is 90%, the wavelengths at which the filter achieves 45% transmission will define the upper and lower limits of the FWHM. FWHM’s of 10nm or less are considered narrow band and often used for laser clean-up and chemical detection. FWHM’s of 25 – 50nm are often used in machine vision applications; FHWM’s of more than 50nm are considered broadband and typically used in fluorescence microscopy applications.
BLOCKING RANGE
Blocking Range is wavelength interval used to denote a spectral region of energy that is attenuated by the filter (Figure 2).
The degree of its blocking is typically specified in terms of optical density.
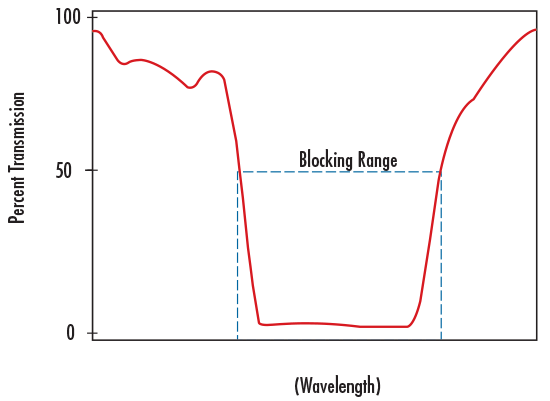
FIGURE 2: ILLUSTRATION OF BLOCKING RANGE
SLOPE
Slope is a specification often defined on edge filters, such as short pass or long pass filters, to describe the bandwidth over which the filter transitions from high blocking to high transmission. Given as the percent of the cut-wavelength, slope can be specified from a variety of starting and end points.
OPTICAL DENSITY
Optical Density (FIGURE 3) describes the amount of energy blocked or rejected by a filter. A high optical density value indicates low transmission, and low optical density indicates high transmission. Optical densities of 6 or greater are used for extreme blocking needs such as Raman spectroscopy or fluorescence microscopy. Optical densities of 3.0 – 4.0 are ideal for laser separation and clean-up, machine vision, and chemical detection, while optical densities of 2.0 or less are ideal for color sorting and separating spectral orders.
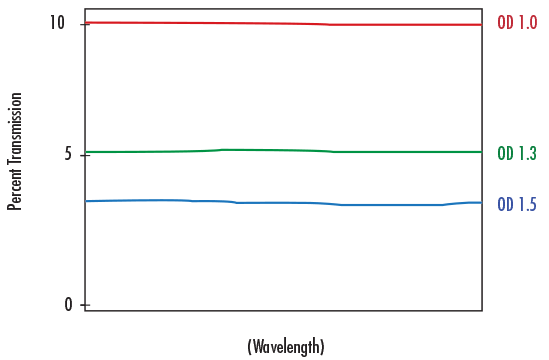
FIGURE 3: ILLUSTRATION OF OPTICAL DENSITY
CUT-ON WAVELENGTH
Cut-On Wavelength is a term used to denote the wavelength at which the transmission increases to 50% throughput in a long pass filter.
Cut-on wavelength is indicated by λ cut-on in Figure 4.
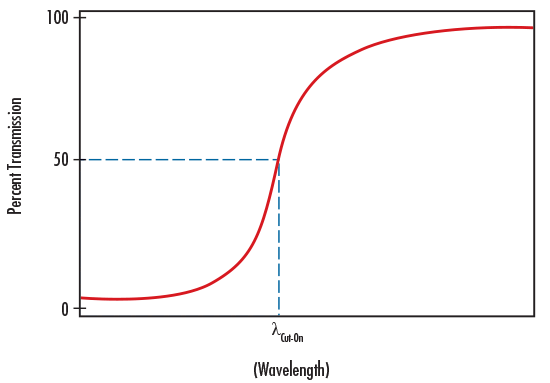
FIGURE 4: ILLUSTRATION OF CUT-ON WAVELENGTH
CUT-OFF WAVELENGTH
Cut-Off Wavelength is a term used to denote the wavelength at which the transmission decreases to 50% throughput in a short pass filter.
Cut-off wavelength is indicated by λ cut-off in Figure 5.
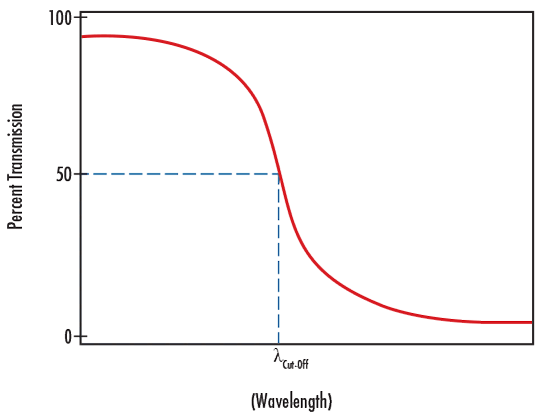
FIGURE 5: ILLUSTRATION OF CUT-OFF WAVELENGTH
VY Optoelectronics Co.,Ltd. can supply a full range of filter.
They are short pass Filter, long pass Filter, band pass Filter, ultraviolet Filter, infrared Filter, heat absorbing Filter, and color temperature conversion filters.
We use material by China to Schott, Hoya, and other manufacturers to process them. Metallic films, colored glasses and thin dielectric films filter are all available per your requirements.
People also ask
- What is the difference between absorption filter and interference filter?
Absorption Filters. Explore how gelatin and glass absorption filters are used to pass a specific band of wavelengths. Interference Filters - These filters differ from absorption filters in the fact that they reflect and destructively interfere with unwanted wavelengths as opposed to absorbing them.
- What are the advantages of heat absorbing glass?
The tinted heat-absorbing glass has been wrought to absorb the excessive heat at the exterior of a building, thereby keeping the interiors cool and saving on air conditioning costs. This absorptive property keeps the rooms cooler without additional efforts.
- What is the best glass to stop heat?
Toned glass – A tint is applied to the glass during manufacture to reduce the amount of heat transmitted through it. Tinted, or toned glass can also reduce light and heat gain in winter as well as Summer. Reflective coatings – Can be applied to new and existing windows.
- What does an optical filter do?
Optical filters are passive optical devices that consist of specialized optical coatings applied onto a substrate. The coatings modify the refractive index of the substrate, enabling them to reflect, transmit, or absorb incoming light depending on its wavelength.
Want to learn more / get a quote? Just click here to contact us now~ 
Related Products
China Manufacturers Supplied HB610 GB39 QB29 Color Glass Filter for Medical Equipment and Camera
Colored glass filters are manufactured by injecting colored dye into a glass ...
High Quality Optical Protective Glass Filter Polarizer Film Sheet
Filters are used to selectively transmit a portion of the light spectrum ...